我々のいる、太陽系誕生の謎に迫る
2020年2月、ニュージーランドのテカポに星を見に行ってきました。
世界最南端「マウント・ジョン天文台」があります。
日本では見られない南半球の星座の世界が広がっています!
南十字星やマゼラン星雲などが輝く満天の星空、
生まれて初めて見た天の川は感激でした!!
天の川は私たちの銀河系を横から見た姿。
宇宙の壮大さを実感!!!筆舌に尽くしがたし!!!
今日は、その銀河系(天の川銀河)の中の太陽系誕生の謎に迫ってみましょう。
VOA記事から。
銀河の衝突が太陽系を作ったかもしれない(和訳)
Crash of Galaxies May Have Created Solar System
巨大な規模の暴力的な出来事が 太陽系の誕生につながったのかもしれないと 科学者たちは言います 。その出来事は2つの銀河の衝突でした。
私たちの銀河系と小さな銀河系が一緒になったことで、45億年以上前に無数の星が天の川に形成された、と科学者たちが先週報告しました。
小さい方の銀河は、射手座と呼ばれています。天の川銀河よりも1万倍も小さいのです。
銀河同士が衝突しても、通常は星同士がぶつかることはない、と科学者たちは指摘しています。しかし、衝突は星形成のための条件を作り出すことができます。例えば、銀河のガスの量が増えたり、ガス雲が集まってきたりすることがあるのです。
ロイター通信によると、2つの銀河は60億年以上前に初めて衝突したといいます。それ以来、いて座は天の川とその1000億個近くの星をさらに2回通過しています。科学者たちは、この3つの出来事を、天の川銀河の星形成の急激な飛躍と結びつけています。
科学的データによると、62億年前から42億年前までの長い星形成期間が、最初の衝突につながっていたことが判明しました。このデータは、欧州宇宙機関のガイア宇宙観測所から得られたものです。科学者たちは、衝突した銀河に関連して、19億年前と10億年前の2つの星形成波が起こったと考えてます。それぞれ数億年前に起こったと考えられています。
トマス・ルイス ララ氏は、スペインのカナリアス・アストロフィジカ研究所の天文学者です。彼は、この研究に関する報告書の筆頭執筆者です。
彼によると、銀河の衝突は自動車の衝突とは違うといいます。射手座と天の川の一部が交差することはありますが、星同士の衝突は「本当に、本当にまれなこと」だと彼は言います。
その"衝突 "は、私たちの銀河の星形成の速度を変えた、とルイス ララ氏は説明しています。
「第一に、我々は、新しい星を形成するために我々の銀河のガスの量を増加させる射手座から 追加の物質、ガスを手にしているのです。 」と彼は言います。第二に、射手座からのガス雲と天の川からのガス雲の衝突があり、これも星の形成につながっているのです。第三に、衝突によって重力的な不安定性が生じ、それが星形成につながることがある、と同氏は述べています。これは、通常は密度の低い星系間の空間に存在するガス状物質の密度が変化するために起こります。
銀河相互作用に関する報告は、出版物「Natural Astronomy」に掲載されています。
銀河系と太陽系
ざっくり、中学3年理科のおさらい
銀河系または天の川銀河は太陽系を含む銀河の名称です。
夏に夜空を見上げると、北から南に横ぎる雲のような光の帯を見ることができますね。これが七夕で有名な「天の川」です、実は私たちの太陽系がある銀河なのです。他の銀河とは区別して、「銀河系」または「天の川銀河」とよびます。
1000臆~2000臆個の恒星(太陽のように自分で光る星)で構成された平べったい集まりーこれが銀河系。その端から端までは10万光年。その銀河系の中心から3万光年にあるのが太陽、太陽の周りをまわる太陽系。その太陽系の惑星の一つが地球ですね。
ーーーーーーーーざっくり解説、こんなでしたかね。-----
まずは宇宙の大き体感ください☟
銀河系を上から見ると
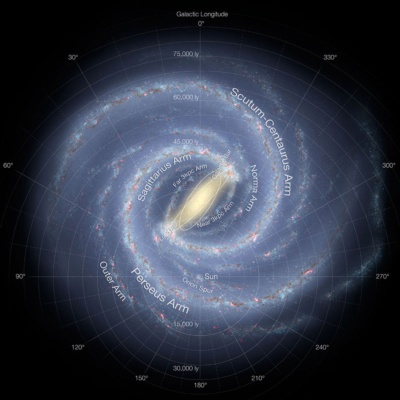 出典:NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC
出典:NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC
下記のNATIONAL GEOGRAPHICをご参照ください。
銀河系は大きかった、そして銀河の数は計り知れず。
今宵の満月、ストロベリームーンを眺めながら、
ひととき夜空に身を任せましょう。
Crash of Galaxies May Have Created Solar Syst (原文)
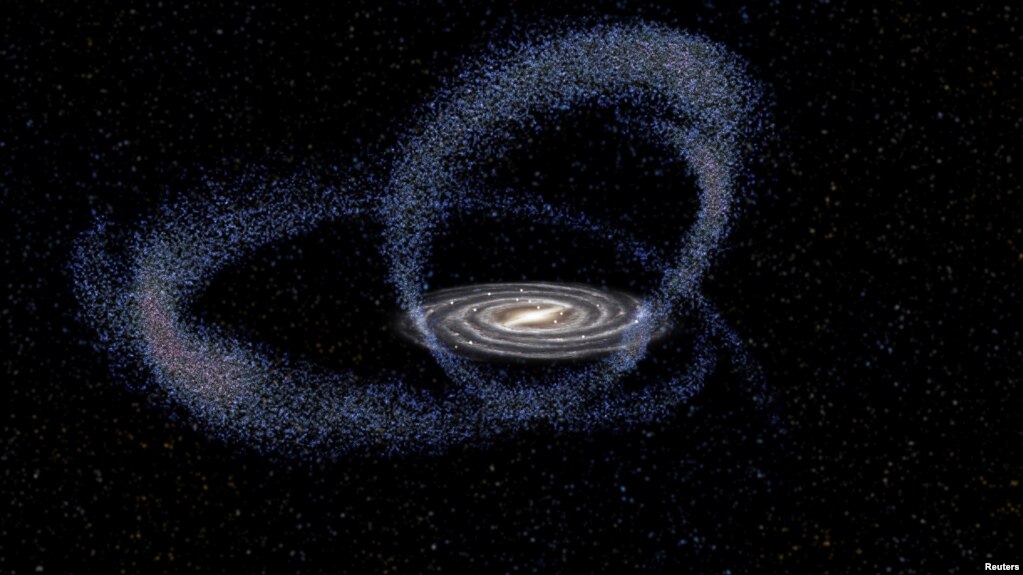

The coming together of our galaxy and a smaller one caused countless stars to form in the Milky Way more than 4.5 billion years ago, scientists reported last week.
The smaller galaxy is called Sagittarius. It is 10,000 times smaller than the Milky Way.
A crash between galaxies usually does not involve stars hitting each other, the scientists noted. But it can create conditions for star formation. For example, it can increase the amount of gas in a galaxy or cause gas clouds to come together.
The Reuters news agency says the two galaxies first crashed more than six billion years ago. Since then, Sagittarius has passed through the Milky Way and its nearly 100 billion stars two more times. The scientists link all three events to a sharp jump in Milky Way star formation.
Scientific data show a long period of star-formation -- from 6.2 billion to 4.2 billion years ago -- linked to the first crash. That data comes from the European Space Agency’s Gaia space observatory. Scientists believe two other star-formation surges linked to the colliding galaxies took place 1.9 billion years ago and 1 billion years ago. Each one lasted a few hundred million years.
Tomás Ruiz-Lara is an astronomer at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias in Spain. He was the lead writer of a report on the research.
He says galaxy crashes are not like car crashes. Some parts of Sagittarius and the Milky Way intersect, but a crash between stars would be “really, really rare,” he said.
The “crash” changed our galaxy’s speed of star formation, Ruiz-Lara explained.
“First, we have the addition of material, gas, from Sagittarius that increases the amount of gas in our galaxy to form new stars,” he said. Second, there is the collision between gas clouds from Sagittarius and gas clouds from the Milky Way, which also led to star formation. Third, the crash causes gravitational instabilities that can lead to star formation, he said. This happens because of changes in the density of the gaseous matter in the usually low-density space between star systems.
The report on galactic interactions appears in the publication Natural Astronomy.
________________________________________________________________
Words in This Story
solar system - n. our sun and the planets that move around it
galaxy - n. any of the very large groups of stars that makes up the universe
Milky Way - n. the galaxy in which we live that contains the stars that make up the Milky Way
data - n. facts or information used usually to calculate, analyze, or plan something
surge - n. a sudden large increase
intersect - v. to meet and cross at one or more points
instability - n. the state of being likely to change
density - n. the quality of having parts that are close together