Roboats って?
なんか楽しい(^^♪
アムスに2年間ほど住んでいました。
あの運河とこのボート、何かそぐわない気がするけど。。。
とりあえず、
You Tube 見てるだけで楽しい。
アムスの街並みも見れて。
早速今日のVOAニュースより。
Let's enjoy!!
- アムステルダムの自動運転ボートは人や物を移動させることが可能
- MIT CSAIL
- MIT Senseable City Lab
- Urban imagination and social innovation through design & science
アムステルダムの自動運転ボートは人や物を移動させることが可能
Self-Driving Boats in Amsterdam Can Move People and Goods
October 28, 2020
自走車技術の開発とテストは、ここ数年で大きな進歩を遂げています。しかし、エンジニアは他の種類の自律走行車にも取り組んでいます--水のために作られたものも含め--。
マサチューセッツ工科大学、MIT、の研究者は、そのようなプロジェクトの1つをリードしています。エンジニアは、彼らが "ロボート "と呼ぶ自律的な水車を開発してきました。この言葉は "ロボット "と "ボート "を組み合わせたものです。
2016年に始まったこのプロジェクトは、アムステルダムの水路に沿って物資や人を運ぶためのボート群を作ることを目的としています。オランダの首都アムステルダムは、運河の大規模なネットワークがあることから”世界で最も水のある都市”と呼ばれてきました。
このプロジェクトは、自律型ボートがアムステルダムをはじめとする他の都市をいかにより効率的に、住民の生活の質を向上させることができるかを探求するために立ち上げられました。
MITの人工知能研究所であるCSAIL☟が、同大学のSenseable City Lab☟と提携して開発を主導しているます。
エンジニアたちは過去の取り組みの中心に、小物を運ぶために設計された自律型のボートを置いていました。しかし、このプロジェクトの最新作であるロボートIIは、乗客を運ぶこともできます。
開発者たちは、自動運転車の訓練に使われるのと同じような機械学習の手法を使いました。このロボットボートは、人や物資を運ぶだけでなく、”他のロボートと接続して自律的なプラットフォームの範囲を形成する”ように設計されています、とダニエラ・ルス氏は声明で語っています。彼女はMITの教授であり、CSAILのディレクターでもあります。
電気駆動のロボートIIは、それが任意の方向に移動することを可能にする4つのプロペラを持っています。それは一連のカメラとその動きを導くためのセンサーが装備されています。また、光レーザーを使って環境をマッピングし、距離を測定する技術であるLiDARを使用しています。
このボートは、センサーで収集したデータを使用して、”一連のゴール地点間の動線を操縦する”ように設計されていると研究者は言います。
ロボートIIは、2メートル×1メートルの大きさで、重さは約80キログラム。模型のデモビデオでは、2人の乗客を乗せている様子が映し出されています。
MITのチームは現在、3台目の自律型水上ビークルを開発中です。そのボートは長さ4メートルで、最大6人の乗客を乗せることができるように設計されています。
研究者たちは、オンラインで公開された論文の中で、最新の開発とテストの結果を説明しています。彼らは、ロバットIIがデータを収集しながら3時間、アムステルダムの運河を自律的に航行することに成功したと述べています。船は選択したコースを完了し、わずか0.17メートルの誤差でスタート地点に戻った、とエンジニアは報告しています。
チームによると、自律システムは、別々のボートが一緒に作業するように設計されているといいます。例えば、ロボートIIの車両は、リーダーボートによって導かれたより大きなグループでリンクアップすることができる、と研究者は言います。後続のボートは、リーダーボートの隣に、その前に、またはその後ろに移動することができます。この能力は、物品を輸送することを意味する自律走行車の可能性を大幅に拡大することができます。
MITのチームは、その最大の自律型ボートのモデルを作成するために、最初の2つのロバットから学んだことを使用することをすでに計画しています。研究者たちはそのボートをアムステルダムでもテストする予定です。その後、チームは、海の中で見られるような ”より騒がしい水域”の環境での実験を開始する予定です。
自律航行型の船の実験はすでにいくつか行われています。9月には、メイフラワー自律船と呼ばれる海洋調査船が、船長や乗組員を乗せずに大西洋を航行しようとすることが発表されました。
全長15メートルのこの船は、海洋研究グループのプロマーレと米コンピューター企業IBMの共同プロジェクトです。この船は、1620年にヨーロッパの入植者のグループを北米に運んだメイフラワー号と同じ道を大西洋を横断することになります。この横断は来年の初めに開始される予定です。
新しいメイフラワー号の建造者は、将来的には、このような船を使って、人が到達するのが困難であったり、危険であったりする海の地域を探索することができるようになることを期待していると述べています。
MIT CSAIL
MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory pioneers research in computing that improves the way people work, play, and learn.
MITのコンピュータサイエンス・人工知能研究所は、人々の働き方、遊び方、学び方を改善するコンピューティングの研究を先駆的に行っています。
MIT Senseable City Lab
Urban imagination and social innovation through design & science
The real-time city is real! As layers of networks and digital information blanket urban space, new approaches to the study of the built environment are emerging. The way we describe and understand cities is being radically transformed—as are the tools we use to design them. The mission of the Senseable City Laboratory—a research initiative at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology—is to anticipate these changes and study them from a critical point of view.
Not bound by the methodologies of a single field, the Lab is characterized by an omni-disciplinary approach: it speaks the language of designers, planners, engineers, physicists, biologists and social scientists. Senseable is as fluent with industry partners as it is with metropolitan governments, individual citizens and disadvantaged communities. Through design and science, the Lab develops and deploys tools to learn about cities—so that cities can learn about us.
MIT’s Senseable City Lab is against racism and all forms of discrimination. We encourage applications from minorities and other under-represented groups.
デザイン&サイエンスによる都市の想像力と社会イノベーション
リアルタイム都市はリアルだ! ネットワークとデジタル情報の層が都市空間を覆い尽くす中で、建築環境の研究に対する新しいアプローチが生まれつつあります。私たちが都市を記述し、理解する方法は、都市を設計するために使用するツールと同様に、根本的に変容しつつあります。マサチューセッツ工科大学の研究イニシアチブであるSenseable City Laboratoryの使命は、このような変化を予測し、批判的な視点から研究することです。
一つの分野の方法論に縛られず、学際的なアプローチを特徴とし、デザイナー、プランナー、エンジニア、物理学者、生物学者、社会科学者の言語を話す。Senseableは、産業界のパートナーと同様に、大都市政府、個人市民、恵まれない地域社会との連携にも精通しています。デザインと科学を通じて、都市について学ぶためのツールを開発・展開し、都市が私たちについて学ぶことができるようにします。
MITのSenseable City Labは人種差別やあらゆる形態の差別に反対しています。マイノリティやその他の不登校のグループからの応募を奨励しています。
Self-Driving Boats in Amsterdam Can Move People and Goods
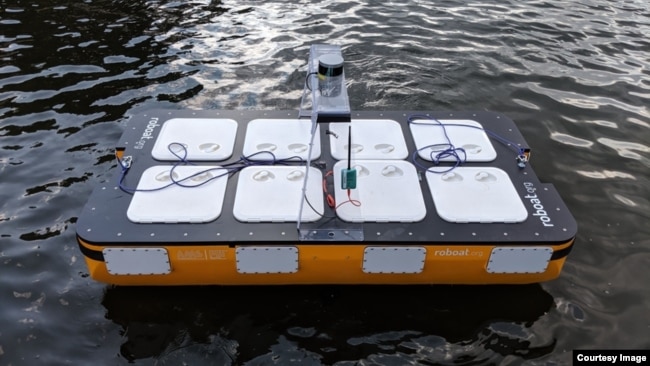 This photograph shows the latest version of MIT's autonomous boat - Roboat II, which is two meters long and is capable of carrying passengers. (Photo: MIT/CSAIL researchers)
This photograph shows the latest version of MIT's autonomous boat - Roboat II, which is two meters long and is capable of carrying passengers. (Photo: MIT/CSAIL researchers)
The development and testing of self-driving car technology has seen major progress in recent years. But engineers are working on other kinds of autonomous vehicles too -- including some built for water.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT, are leading one such project. The engineers have been developing autonomous water vehicles they call “roboats.” The word is a combination of “robot” and “boat.”
The project – which began in 2016 – aims to create a group of boats to transport goods and people along the waterways of Amsterdam. The Dutch capital has been called the world’s “most watery city” because of its large network of canals.
The project was launched in an effort to explore how autonomous boats can make Amsterdam - and other cities - more efficient and improve the population’s quality of life.
MIT’s Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, CSAIL, is leading the development in a partnership with the university’s Senseable City Lab.
The engineers centered past efforts on autonomous boats designed to transport small goods. But the project’s latest creation, the Roboat II, can also carry passengers.
The developers used machine-learning methods similar to those used to train self-driving cars. The robotic boats are designed to not only carry people and goods, but also “connect with other Roboats to form a range of autonomous platforms,” Daniela Rus said in a statement. She is a professor at MIT and the director of CSAIL.
The electric-powered Roboat II has four propellers that permit it to move in any direction. It is equipped with a series of cameras and sensors to guide its movements. It also uses LiDAR, a technology that uses light lasers to map the environment and measure distances.
The boats are designed to use the sensor-collected data to create and “pilot a path between a series of goal points,” the researchers say.
The Roboat II measures two meters by one meter and weighs about 80 kilograms. A demonstration video of the model showed it carrying two passengers.
The MIT team is currently developing its third autonomous water vehicle. That boat is expected to be four meters long and is designed to carry up to six passengers.
The researchers described their latest development and testing results in a paper published online. They said Roboat II was successful in autonomously navigating the canals of Amsterdam for three hours while collecting data. The boat completed its chosen course and returned to the starting point with an error of just 0.17 meters, engineers reported.
The team says it designed its autonomous system to involve separate boats working together. For example, Roboat II vehicles can link up in larger groups guided by a leader boat, the researchers say. The follower boats can travel next to the leader boat, in front of it or in back of it. This ability can greatly expand the possibilities of autonomous vehicles meant to transport goods.
The MIT team plans to use what it has learned from its first two Roboats to create a model of its biggest autonomous boat yet. The researchers will test that boat in Amsterdam, as well. After that, the team plans to start testing the vehicles in environments with “more noisy waters,” such as conditions found in the ocean.
There have already been some experiments with autonomous shipping vehicles. In September, it was announced that an ocean research vehicle called the Mayflower Autonomous Ship would attempt to set sail across the Atlantic without a captain or crew on board.
The 15-meter ship is a joint project of ocean research group ProMare and IBM, the American computing company. It will take the same path across the Atlantic as the 1620 Mayflower - the ship that carried a group of European settlers to North America. The crossing is planned to begin early next year.
The builders of the new Mayflower say they hope such ships can be used in the future to explore parts of oceans that are too difficult or dangerous for people to reach.
____________________________________________________________
Words in This Story
autonomous – adj. independent and having the power to operate automatically without human involvement
canal – n. an artificial river built for boats to travel along or to take water where it is needed
efficient – adj. working well and not wasting time or energy
range – n. a group of different things of the same general kind
platform – n. a vehicle used for a particular purpose or to carry a specified kind of equipment
propeller – n. piece of equipment made of two or more flat metal pieces that turn around and cause a ship or aircraft to move
navigate – v. to determine the correct sea or land route
captain – n. the person in control of a ship or aircraft
error – n. a mistake