🎍明けましておめでとうございます🎍
今年もVOAで世界の今を英語と共に学習したいと思います。
尽きぬ科学研究の探求は、尽きぬ語学学習と同様ですね。
zeptosecond、驚きを持って聴いたのを覚えています!
さぁ、どんな科学の進展があったのか、2020タイムトラベルしましょう。
(enzymes:酵素、を頭の片隅に入れて)
今日のVOA,2020新しい科学の発見の旅へ!!!
Let's get started!!!
2020年の新科学発見
New Scientific Discoveries Made in 2020
1 hour ago /2021/1/03
2020年、世界のトップ科学者の多くが、新しいコロナウイルスに注目しました。彼らの努力は、ウイルスについての貴重な情報を提供し、ウイルスと戦うための新しいワクチンにつながりました。
しかし、2020年には他にも大きな科学的発展がありました。ここでは、私たちがこの1年間に取り上げた注目すべき科学の話をいくつか振り返ってみましょう。
プラスチックを食べるバクテリア
ヨーロッパの研究者たちは、リサイクルや破壊が困難なプラスチックの一種であるポリウレタンを餌とする新しい細菌を発見した。
ドイツのヘルムホルツ環境研究センターの研究チームは、この発見が、世界の埋め立て地を埋め尽くし、海を汚染するリサイクル困難なプラスチックの洪水を減らすのに役立つ可能性があると述べています。
ポリウレタンベースの製品の多くは、環境に危険な化学物質を放出する可能性があります。しかし、研究者たちは、細菌が材料を分解するための酵素を生成することができることを発見しました。
2070年までに’生きられない’暑さ
アメリカ、中国、ヨーロッパの研究者は、わずか50年後には、35億人もの人々が”生活できないほどの暑さ”に直面する可能性があると警告しています。
研究では、人間が原因の気候変動とリンクした世界の気温の上昇が、酷暑の原因になることを示唆しています。危険にさらされている人々の正確な数は、汚染物質のレベルを削減できるかどうか、世界の人口がどのくらいの速さで増加するかに左右されます。
人口増加と炭素汚染の最悪のケースを予測した場合、2070年までに約35億人が猛暑地域に住むことになるだろうと、この研究では推定しています。これは世界の予測人口の3分の1に相当します。
雪を作るための雲の種まき
科学者たちは、新しい測定方法を使って、雲の種まきが適切な条件で雪を作り出すことができることを確認したと述べています。雲の種まきとは、雲の中に様々な物質を注入して雨や雪、氷を作り、それを地上に降らせることです。
アメリカの研究者らは、アイダホ州で行われた実験で、レーダーなどを使って降雪量を測定したと発表しました。
研究者によると、いくつかのケースでは、雲の種まき作業によって、対象地域全体の降雪量が測定可能なほど増加したといいます。
場合によっては、自然の雪が存在しない場所に新たな降雪が発生したこともありました。ある雲の種まき作業では、約67分間降雪をもたらす落下量が発生しました。
Neowise comet ネオワイズ彗星
ネオワイズと呼ばれる彗星は、世界中の人々に素晴らしい光のショーを提供しました。
彗星は氷、岩石、塵でできた太陽系の天体です。科学者たちは、ネオワイズ彗星の大きさを約5kmと推定しています。それは、25年間で北半球の上空に現れた最も明るい彗星でした。
多くの国のソーシャルメディアのユーザーは、彗星が頭上の空を照らす様子を撮影した画像を投稿しました。
宇宙の3Dマップ
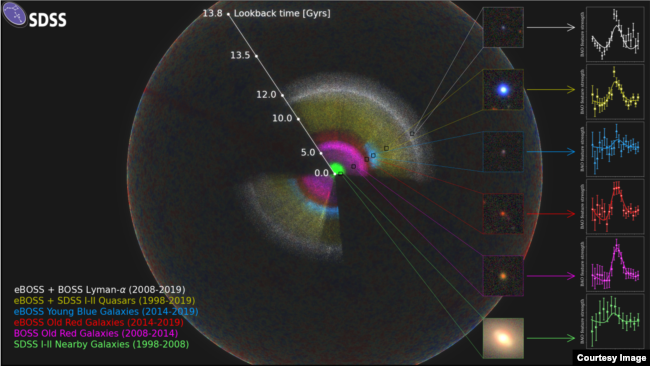
SDSSの地図は、観測可能な宇宙(宇宙マイクロ波背景の変動を示す外側の球体)の中に位置する虹のように示されています。(Anand Raichoor (EPFL)、Ashley Ross (オハイオ州立大学)、SDSS コラボレーション)
科学者たちは、これまでに作成された宇宙の最大の3次元、つまり3D地図を発表しました。
この20年間のプロジェクトは、アメリカのニューメキシコ州にある望遠鏡から収集したデータを使って宇宙の地図を作成することを目的としています。研究者によると、3D地図は200万個以上の銀河とクェーサーの測定値を作成したといいます。
クェーサーとは、”超巨大ブラックホールに物質が落下して光を放つ明るい銀河”と定義されています。
世界最古の動物

Kampecaris obanensisと呼ばれ、スコットランドで出土した4億2500万年前のミリピードの化石が、2020年5月27日にロイターに公開されたこの日付なしの資料写真に写っています。英国地質調査所/ロイター経由資料
科学者たちは5月に、最も古くから知られている陸生動物と考えられているものを発見したと発表しました。ミリマムシのような生物の遺骸はスコットランドで発見されました。
研究者によると、この小型で化石化した生物は約4億25000万年前のものと推定されています。この生物は、後に陸上で生活する多くの動物への道を導いたのかもしれません。
この生物は化石から発見された最古の陸上動物ですが、土壌ミミズはその前に生息していたと考えられており、おそらく4億5000万年前に生息していたと考えられます。
’ゼプト秒’を初めて測定
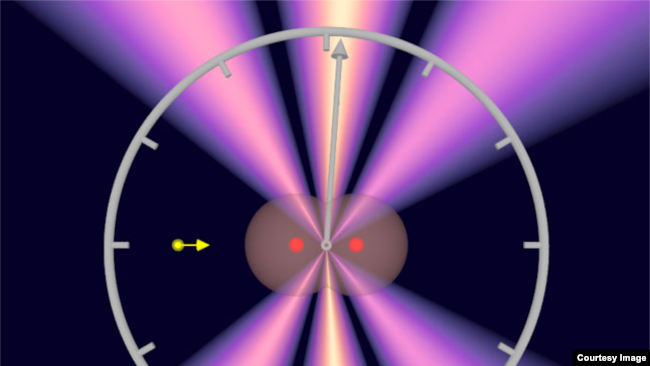
この画像は、これまでに記録された中で最も小さな時間の単位の測定に成功したと言うドイツの研究者が行った科学実験を表しています。写真:スヴェン・グルンドマン(フランクフルト・ゲーテ大学)
ドイツの科学者たちは、これまでに記録された中で最小の時間の単位、ゼプト秒を測定したと発表しました。ゼプト秒とは、10億分の1秒の1兆分の1です。
研究者たちは、光の粒子である光子が水素分子を横切るのにどれくらいの時間がかかるかを研究しているときに、この発見をしました。研究者らによると、光子は約247ゼプト秒で分子を横切ったといいます。「これは、これまでに測定に成功した中で最も短い時間です」と、研究チームは声明で述べています。
New Scientific Discoveries Made in 2020
 The comet Neowise or C/2020 F3 is seen behind an Orthodox church over the Turets, Belarus, 110 kilometers (69 miles) west of capital Minsk, early Tuesday, July 14, 2020. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)
The comet Neowise or C/2020 F3 is seen behind an Orthodox church over the Turets, Belarus, 110 kilometers (69 miles) west of capital Minsk, early Tuesday, July 14, 2020. (AP Photo/Sergei Grits)
In 2020, many of the world’s top scientists centered their attention on the new coronavirus. Their efforts provided valuable information about the virus and led to new vaccines to fight it.
But there were other big scientific developments in 2020, as well. Here is a look back at some of the notable science stories we covered during the past year.
Plastic-eating bacteria
European researchers identified a new bacterium that feeds on polyurethane, a kind of plastic that is difficult to recycle or destroy.
The team, from Germany’s Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research, said the discovery could help reduce a flood of hard-to-recycle plastics filling up the world’s landfills and polluting oceans.
Many polyurethane-based products can release dangerous chemicals into the environment. But the researchers found that the bacterium can produce enzymes to break down the material.
‘Unlivable’ heat by 2070
Researchers from the United States, China and Europe warned that in just 50 years, as many as 3.5 billion people could be facing “near-unlivable” heat.
A study suggests the extreme heat would result from rising world temperatures linked to human-caused climate change. The exact number of people at risk will depend on whether pollutant levels can be reduced and how quickly the world population will grow.
Under the worst-case predictions for population growth and carbon pollution, the study estimates about 3.5 billion people could be living in extremely hot areas by 2070. That would be one-third of the world’s projected population.
Cloud seeding to produce snow
Scientists said they used new measuring methods to confirm that cloud seeding can produce snowfall under the right conditions. Cloud seeding involves injecting various substances into clouds to produce rain, snow or ice that falls to the ground.
American researchers announced they had used radar and other instruments to measure snowfall levels during experiments carried out in the state of Idaho.
The researchers said that, in several cases, cloud seeding operations measurably increased snowfall across targeted areas.
In some cases, the seeding created new snowfall where no natural snow existed. One cloud seeding operation resulted in precipitation that produced snowfall for about 67 minutes.
 The Comet Neowise or C/2020 F3 is seen before sunrise over Balatonmariafurdo, Hungary, Tuesday, July 14, 2020. It passed closest to the Sun on July 3 and its closest approach to Earth will occur on July 23. (Gyorgy Varga/MTI via AP)
The Comet Neowise or C/2020 F3 is seen before sunrise over Balatonmariafurdo, Hungary, Tuesday, July 14, 2020. It passed closest to the Sun on July 3 and its closest approach to Earth will occur on July 23. (Gyorgy Varga/MTI via AP)
Neowise comet
A comet called Neowise provided excellent light shows for people across the world.
Comets are solar system objects made up of ice, rock and dust. Scientists estimated Neowise was about 5 kilometers across. It was the brightest comet to appear above the Northern Hemisphere in 25 years.
Social media users in many countries posted images they captured of the comet as it lit up the sky over their heads.
3D map of universe
Scientists released the largest three-dimensional, or 3D map of the universe ever created.
The 20-year project aims to map the universe using data collected from a telescope in the American state of New Mexico. Researchers said the 3D map produced measurements of more than two million galaxies and quasars. Quasars are defined as “bright galaxies lit up by material falling onto a central supermassive black hole.”
World’s oldest known animal
Scientists said in May they had discovered what is believed to be the oldest-known land animal. Remains of the millipede-like creature were found in Scotland.
Researchers said the small, fossilized creature is estimated to be about 425 million years old. It may have helped lead the way for the many animals that would later live on land.
While the creature is the earliest land animal known from a fossil, soil worms are believed to have lived before them – possibly 450 million years ago.
‘Zeptosecond’ measured for first time
German scientists announced they had measured the smallest unit of time ever recorded - a zeptosecond. A zeptosecond is one trillionth of a billionth of a second.
Researchers made the discovery while studying how long it took a photon – a particle of light – to cross a hydrogen molecule. They said the photon crossed the molecule in about 247 zeptoseconds. “This is the shortest timespan that has been successfully measured to date,” the team said in a statement.
__________________________________________________
Words in This Story
recycle – v. to reuse something that has been used before often in another way
enzyme – n. a chemical substance produced by living cells that makes particular chemical reactions happen in animals and plants
precipitation – n. rain or snow falling to the ground
three-dimensional – adj. appearing to have length, depth and width
galaxy – n. a large group of stars from the same universe
millipede – n. a small creature that is like an insect and that has a long, thin body with many legs
fossilized – adj. having been changed into a fossil. A fossil is something (such as a leaf, skeleton, or footprint) that is from a plant or animal that lived in ancient times
unit – n. a single thing or a separate part of something larger
timespan – n. a period of time within which something happens, or a period between two events


