医学は本当に目覚しく進歩しているのですね。
今年初め、世界初の遺伝子操作した豚の心臓移植のニュースが世界を駆け巡りました。残念ながらその約2ヶ月後となる3月8日に亡くなったと手術担当したメリーランド大学医学部から発表でした。原因は明らかになっていませんが、一筋の光であることに変わりはありません。
そして今回のこのニュース。注目するのは抗拒絶反応薬としての胸腺組織移植です。臓器移植した友人がいるので、抗拒絶反応薬との対応の大変さを知ってからです。
VOAで英語を学び、世界の今を見つめましょう!!
心臓移植の実験的手術後、赤ちゃんは順調に成長(和訳)
Baby Doing Well after Experimental Heart Replacement Operation
March 11, 2022
米国ノースカロライナ州のデューク大学の医師は、新しい種類の心臓置換手術を受けた男児が元気であることを発表しました。
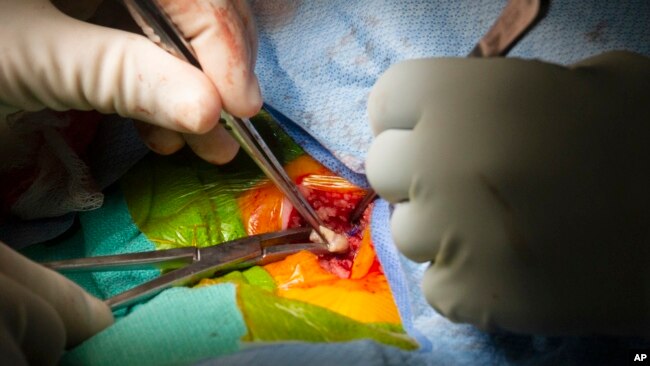
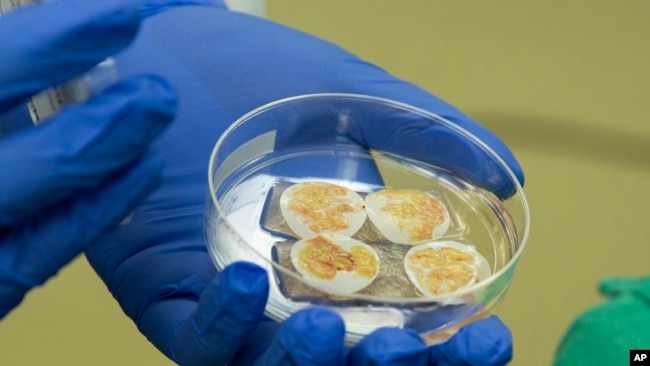
この心臓移植手術には、新しい臓器に対する拒絶反応を防ぐための特別な組織が含まれているとのことです。この組織(thymus gland)は他人の胸腺から採取したもので、実験室で部分的に培養されたものです。
胸腺は人体の感染症や病気と戦う免疫システムにおいて重要な役割を果たす臓器です。医師たちは、提供された臓器に適合する胸腺組織を移植すれば、抗拒絶反応薬を必要とせずに胸腺が生き延びることができるのではないかと考えてきました。この薬は体に害を及ぼす可能性があるのです。
ノースカロライナ州アッシュボロに住むイーストン・シナモン君は、昨年の夏、生後6ケ月で移植を受けました。しかし、デューク大学は胸腺移植がうまくいくかどうかが判明するまで、この手術を発表するのを待っていました。この胸腺移植によって、子供の新しい心臓を異物として扱わないような免疫細胞が作られ始めることを期待したのです。
ジョセフ・トゥレック博士によれば、しばらくしてから、医師はイーストン君を移植後に必要とされる免疫抑制剤から外すことを試みるとのことです。彼はデューク大学の小児心臓外科の責任者です。
この研究は非常に初期の段階です。この研究は、移植に対する免疫寛容と呼ばれるものを作り出すために、科学者が試している可能性のある方法の一つです。トゥレック氏によれば、もしこの方法がうまくいけば、心臓だけでなく他の臓器移植でも試すことができるだろうとのことです。
イーストン君がこの実験的移植の候補になったのは、彼が二つの別々の健康問題を抱えていたからです。彼は生まれつき心臓に問題があり、生まれてすぐの手術では解決できませんでした。そして、彼は度重なる感染症にかかり、医師は彼自身の胸腺が正しく機能していないことに気づいたのです。
胸腺は、T細胞として知られる免疫系の一部の発達を助けるもので、生まれつきない赤ちゃんもいます。デューク大学の研究者たちは、Enzyvant Therapeutics社と共同で、提供された胸腺組織を使って実験室で培養した移植片を開発してきました。
実際、イーストン君は2回の手術を受けました。まず、外科医が新しい心臓を移植し、その間に提供された胸腺は研究所に送られました。その2週間後に、加工された胸腺組織を移植する2回目の手術が行われたのです。新しい免疫細胞を作るために、部分的に働いている自分の胸腺は取り除かれました。
約半年後の検査では、胸腺組織がイーストン君に新しい、よく働くT細胞を作っていることが分かった、とツレック氏は言っています。
Baby Doing Well after Experimental Heart Replacement Operation
Doctors at Duke University in the American state of North Carolina announced that a baby boy is doing well after a new kind of operation to replace his heart.
The heart transplant operation, doctors said, included special tissue to help prevent rejection of the new organ. The tissue came from another person’s thymus gland and was partly grown in a laboratory.
The thymus gland is an organ that plays an important part in the immune system, which fights infection and disease in the human body. Doctors have wondered if implanting thymus tissue that matched a donated organ might help it survive without requiring anti-rejection medicines. Those medicines can have harmful effects on the body.
Easton Sinnamon of Asheboro, North Carolina received his transplant last summer when he was 6 months old. But Duke University waited to announce the operation until after doctors learned whether the thymus implants were working. They hoped the implants would begin producing immune cells that do not treat the child’s new heart like foreign tissue.
After some time, doctors will try taking Easton off the immune-suppressing drugs required after a transplant, said Dr. Joseph Turek. He is Duke University’s head of children’s heart surgery.
The research is in its very early stages. It is one possible method scientists are testing to produce what is called immune tolerance to a transplant. Turek said, if it works, the method could be tried with other organ transplants, not just the heart.
Easton was a candidate for the experimental transplant because he had two separate health problems. He was born with some heart problems that surgeries right after birth failed to solve. And he suffered repeated infections that doctors realized meant his own thymus was not working correctly.
Some babies are born without a thymus, which helps in development of part of the immune system known as T cells. Duke researchers had been working with Enzyvant Therapeutics to develop implants grown in a laboratory with donated thymus tissue.
In fact, Easton received two operations. First, surgeons implanted his new heart while the donated thymus was sent to a laboratory. About two weeks later, he had a second operation to implant the processed thymus tissue. His own partly working thymus was removed so that new immune cells can develop.
About six months later, testing shows the thymus tissue is building Easton new, well-working T cells, said Turek.
Words in This Story
transplant –n./v. The medical operation that replaces an organ in the body with another; to perform a medical operation in which an organ or other part that has been removed from the body of one person is put into the body of another person
stage –n. a particular point or period in the growth or development of something
tolerance –n. (medical) your body's ability to deal with something (such as a drug) so that its effects are experienced less strongly
surgeon –n. (medical) a doctor who performs operations that involve cutting into someone's body in order to repair or remove damaged or diseased parts : a doctor who performs surgery