トキメかずにはいられないー宇宙3D Map
じっとしていられない!!!
ときめかずにはいられない!!!
ドキドキが、ワクワクが止まらない!!
ぜひ映像を見てくださいね。
暑い夏の夜、怪談話で涼をとるのも一興でしょうが、
そこはこれ! 宇宙!! 宇チュー!!
ベッドタイム、天井いっぱいに映しながら眠りに着きたい~。
心は自由に宇宙に羽ばたくーーーーーーーー!!!
先走りましたが、タイトル通り、
今日のVOAニュース。3D Map of the Universe !!
Here we go!!
科学者が宇宙最大の3D地図を公開
Scientists Release Largest 3D Map of the Universe
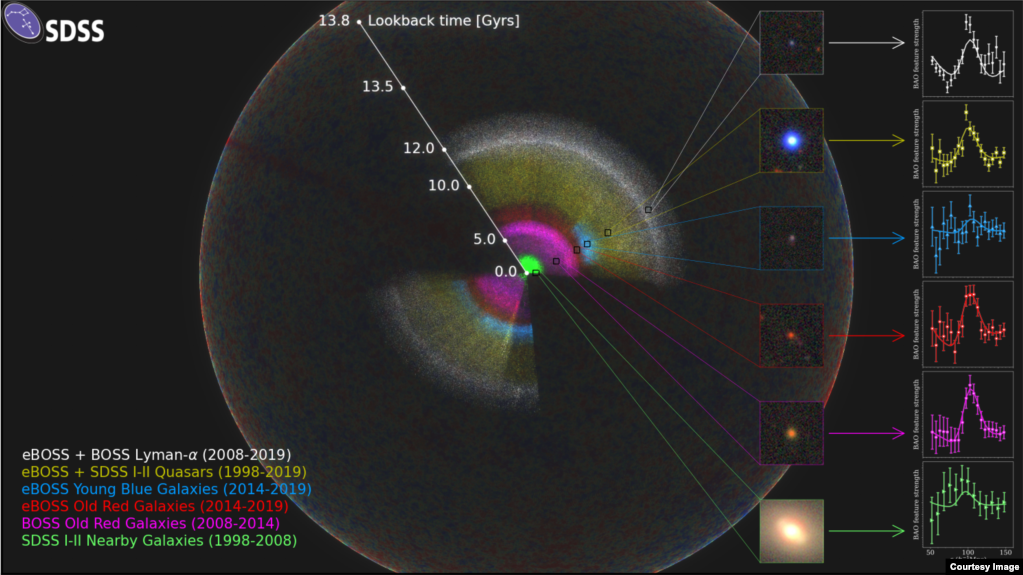 The SDSS map is shown as a rainbow of colors, located within the observable Universe (the outer sphere, showing fluctuations in the Cosmic Microwave Background). (Anand Raichoor (EPFL), Ashley Ross (Ohio State University) and the SDSS Collaboration)
The SDSS map is shown as a rainbow of colors, located within the observable Universe (the outer sphere, showing fluctuations in the Cosmic Microwave Background). (Anand Raichoor (EPFL), Ashley Ross (Ohio State University) and the SDSS Collaboration)
科学者たちは、これまでに作成された宇宙の最大の3次元、つまり3D地図を発表しました。
この地図は、20年以上前に宇宙物理学者の国際的なグループによって立ち上げられたプロジェクトの成果です。このプロジェクトは、アメリカ南西部のニューメキシコ州にある望遠鏡から収集したデータを使って宇宙の地図を作成することを目的としていました。
このプロジェクトでは、これまでに行われた天文学調査の中で最大規模のものの一つであるスローン・デジタル・スカイ・サーベイ(Sloan Digital Sky Survey)の観測データが使用されました。このプロジェクトは、米国を拠点とする非営利科学研究機関であるアルフレッド・P・スローン財団から多額の資金援助を受けています。
研究者によると、新しい3D地図は200万個以上の銀河とクェーサーを測定したといいます。彼らは、クェーサーを”超巨大ブラックホールに物質が落下してすることにより光っている明るい銀河”と定義しました。
主任研究者のウィル・パーシヴァル氏は声明の中で、”宇宙の膨張についての完全な物語”を作成するのに役立ったと述べています。パーシヴァル氏は、カナダのオンタリオ州にあるウォータールー大学の物理学と天文学の教授です。
特に、パーシヴァル氏は、3Dマップが "宇宙の私たちの絵の中の110億年を埋めた "と述べています。
研究チームのもう一人のリーダーは、ユタ大学の物理学・天文学教授のカイル・ドーソン氏。彼は、3Dマップがついに科学者たちに宇宙の歴史にある大きな穴についての情報を提供していると説明しました。
ドーソン氏は声明の中で、「宇宙の古代の歴史も最近の膨張の歴史もかなりよくわかっているが、その中間の110億年には厄介なギャップがある」と述べています。
最新の研究は、この情報のギャップを埋めるのに役立ち、過去10年間の宇宙の研究の中で最も”実質的な進歩”のいくつかを生み出しました、と彼は付け加えています。
宇宙の初期の歴史は、長年の理論モデルと電磁放射の観測のおかげで、はるかに理解されています。銀河の研究や距離測定もまた、数十億年にわたる宇宙の膨張の多くを科学者たちがよりよく理解するのに役立っています。
ローザンヌにあるスイス連邦工科大学の宇宙物理学者ジャン‐ポール・クナイブ氏は、このマッピング・プロジェクトの立ち上げに協力しました。同氏は声明の中で、目標は "宇宙の生涯を通じて、宇宙の最も完全な3D地図を作成すること "だったと述べています。
この地図には、宇宙の構造を構成する要素が示されており、"宇宙がまだ30万年ほどしか経っていない時から "始まっています。これにより、研究者は銀河がどのように位置しているかのパターンを測定することができます。
ダスティン・ラング氏は、カナダのペリメーター研究所の研究センターでこのプロジェクトの研究員を務めています。彼は、新しい3Dマップは、個々の星、銀河、宇宙全体を研究するための努力を大幅に向上させることができると述べています。「一つの実験がこのような科学的遺産を生み出したことは本当に信じられないことです」と。
(ぜひ、体感してくださいね!!)☟わたしの興奮が止まらない
この地図は、宇宙の膨張がある時点からスピードアップし始め、それが続いていることを示唆しています。研究者たちは、これは暗黒エネルギーの存在によって引き起こされているようだと述べています。科学者たちは、この目に見えない要素がアルバート・アインシュタインの一般相対性理論に当てはまると考えています。相対性理論は、重力の法則に関連しており、大きな物体の動きを説明しているのです。
最新の観測結果と初期宇宙の過去の研究を比較すると、膨張率の推定値に違いがあることがわかりました。現在認められている膨張率は、”ハッブル定数”と呼ばれるもので、地球に最も近い銀河間の距離から得られる値よりも10%遅いのです。
Scientists Release Largest 3D Map of the Universe
 The SDSS map is shown as a rainbow of colors, located within the observable Universe (the outer sphere, showing fluctuations in the Cosmic Microwave Background). (Anand Raichoor (EPFL), Ashley Ross (Ohio State University) and the SDSS Collaboration)
The SDSS map is shown as a rainbow of colors, located within the observable Universe (the outer sphere, showing fluctuations in the Cosmic Microwave Background). (Anand Raichoor (EPFL), Ashley Ross (Ohio State University) and the SDSS Collaboration)
Scientists have released the largest three-dimensional, or 3D map of the universe ever created.
The map is the result of a project launched more than 20 years ago by an international group of astrophysicists. The project aimed to map the universe using data collected from a telescope in the southwestern U.S. state of New Mexico.
The effort used observations from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, one of the largest astronomical surveys ever carried out. The project received major funding from the U.S.-based Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, a non-profit science research organization.
Researchers say the new 3D map produced measurements of more than two million galaxies and quasars. The scientists defined quasars as “bright galaxies lit up by material falling onto a central supermassive black hole.”
The measurements helped the team produce a "complete story of the expansion of the universe," lead researcher Will Percival said in a statement. Percival is a professor of physics and astronomy at the University of Waterloo in Ontario, Canada.
Especially, Percival said the 3D map had “filled in 11 billion years in our picture of the universe.”
Another leader of the research team was Kyle Dawson, a physics and astronomy professor at the University of Utah. He explained that the 3D map is finally providing scientists with information about a large hole in the history of the universe.
“We know both the ancient history of the universe and its recent expansion history fairly well, but there’s a troublesome gap in the middle 11 billion years,” Dawson said in a statement.
The latest research has helped fill in that information gap, producing some of the most “substantial advances” in the study of the universe of the past 10 years, he added.
The early history of the universe is much more understood because of years of theoretical models and observations of electromagnetic radiation. Studies of galaxies and distance measurements also helped scientists better understand much of the universe's expansion over billions of years.
Astrophysicist Jean-Paul Kneib of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne helped launch the mapping project. He said in a statement the goal was to produce "the most complete 3D map of the universe throughout the lifetime of the universe."
The map shows the elements making up the structure of the universe, “starting from the time when the universe was only about 300,000 years old.” It permits researchers to measure patterns in how galaxies are positioned.
Dustin Lang is a researcher on the project from Canada’s Perimeter Institute research center. He said the new 3D map can greatly improve efforts to study individual stars, galaxies and the universe as a whole. “It really is incredible that one experiment has produced such a scientific legacy.”
The map suggests that the expansion of the universe began to speed up at some point and has continued to do so. The researchers said this seems to be caused by the presence of dark energy. Scientists believe this unseen element fits into Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity. The theory of relativity relates to the laws of gravity and describes the movement of large objects.
Comparisons between the latest observations and past studies of the early universe have shown differences in the estimated rates of expansion. The currently accepted rate, called the "Hubble constant," is 10 percent slower than the value resulting from distances between galaxies closest to Earth.
________________________________________________________________
Words in This Story
three-dimensional – adj. appearing to have length, depth and width
survey – n. an examination of an area in which its measurements and details are recorded, especially for the purpose of creating a map
galaxy – n. a large group of stars from the same universe
gap – n. an empty hole or space in the middle of something
substantial – adj. large in amount
advance – n. new discoveries and inventions
pattern – n. the way something is often done or repeated
legacy – n. something that is left for people in the future
